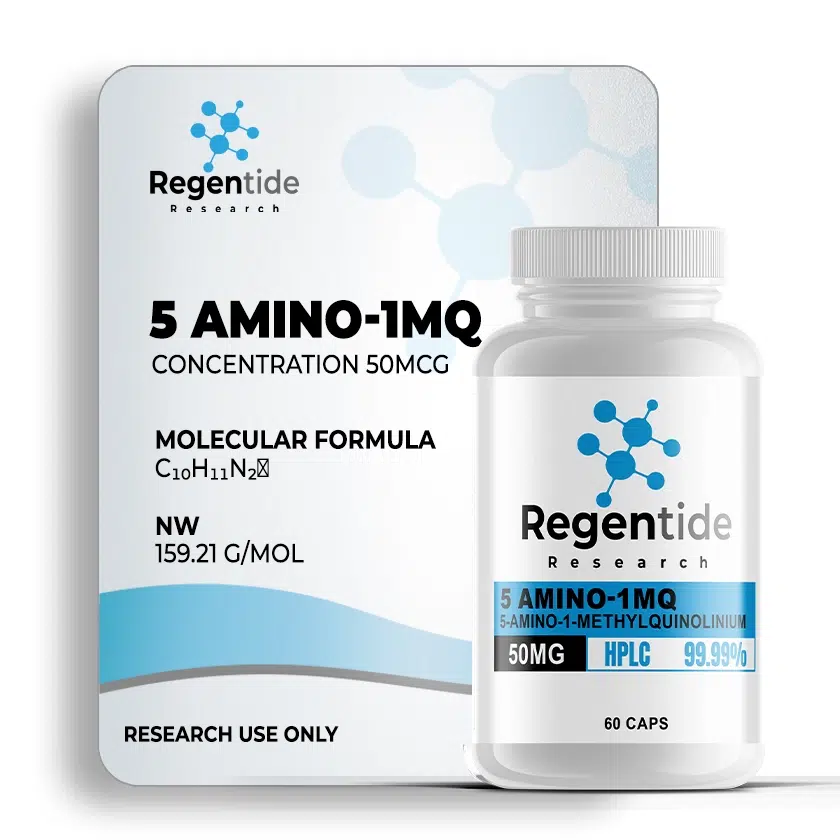
5 Amino-1MQ 50mg (60 caps)
Original price was: $169.99.$142.99Current price is: $142.99.
5-Amino-1MQ – NNMT Inhibitor for Metabolic Research
Product Description:
5-Amino-1MQ is a small, membrane-permeable molecule that acts as a potent inhibitor of Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), an enzyme linked to metabolic function, fat accumulation, and cellular energy regulation. By targeting NNMT, 5-Amino-1MQ has been studied for its potential role in enhancing energy expenditure, reducing fat storage, and supporting NAD+ metabolism—critical factors in metabolic and longevity research.
Key Features:
✔ NNMT Inhibitor – Blocks the enzyme associated with fat accumulation and metabolic disorders.
✔ Supports NAD+ Levels – Helps regulate cellular energy production and mitochondrial function.
✔ Potential Weight Management Research – Studied for its effects on energy balance and fat metabolism.
✔ High Purity & Potency – Ideal for laboratory and experimental applications.
Molecular Formula: C₁₀H₁₁N₂⁺
Molecular Weight: 159.21 g/mol
Note: This product is strictly for research use only. Not for human consumption, medical, or veterinary use.

Description
5-Amino-1MQ – 50mg
5-Amino-1MQ is a small-molecule research compound studied primarily for its inhibitory effect on nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT)—an enzyme involved in methylation pathways that affect cellular metabolism and energy regulation. By targeting NNMT activity, 5-Amino-1MQ has shown potential in preclinical studies to influence pathways related to adipogenesis, mitochondrial function, and NAD+ availability.
NNMT is known to be upregulated in white adipose tissue of obese and insulin-resistant animal models, and its inhibition may restore normal cellular energy balance and metabolic rate. Research suggests that blocking NNMT with 5-Amino-1MQ may promote fat cell shrinkage, increase energy expenditure, and improve glucose utilization in experimental systems.
Chemical Makeup
-
Chemical Name: 5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium
-
Molecular Formula: C10H11N3
-
Molecular Weight: 173.22 g/mol
-
Form: Lyophilized powder
-
Solubility: DMSO, ethanol, water (limited)
Research & Preclinical Investigations
NNMT Inhibition and Fat Cell Metabolism
In vitro and murine studies suggest that 5-Amino-1MQ may inhibit NNMT activity within adipocytes, which in turn may downregulate methylation of nicotinamide and increase intracellular NAD+ levels. This mechanism is proposed to re-activate sirtuin and AMPK signaling pathways, leading to enhanced mitochondrial activity, increased energy output, and potential reductions in adipose volume.
Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis
Experimental models exposed to 5-Amino-1MQ have demonstrated improved insulin sensitivity and reduced fasting glucose levels. The compound appears to support glycemic regulation by promoting the utilization of glucose in peripheral tissues, particularly muscle and liver, through metabolic reprogramming associated with NNMT suppression.
Muscle Regeneration and Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Recent studies have evaluated 5-Amino-1MQ for its role in muscle regeneration and oxidative capacity. In aged or muscle-injured mice, exposure to the compound was correlated with enhanced expression of PGC-1α and mitochondrial transcription factors, indicating a possible role in improving cellular energy metabolism and muscle recovery.
Research Use Only
This compound is provided strictly for in vitro and in vivo laboratory research purposes only. It is not intended for human ingestion, therapeutic applications, or diagnostic procedures. All handling must follow institutional laboratory safety protocols.
References
-
Kraus D, Yang Q, Kong D, et al. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity. Nature. 2014;508(7495):258–262.
-
Parsons R, et al. The role of NNMT and its inhibitor 5-Amino-1MQ in energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):604–618.e5.
-
Hong S, Moreno-Navarrete JM, et al. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase acts as a master metabolic regulator in obesity by controlling NAD+ and SIRT1. Cell Reports. 2015;12(5):722–732.